The major way we learn about human evolution is finding fossils of bones and teeth as well as artifacts. These fossils and artifacts are dated by chemical and physical techniques and then analyzed for what they might imply about people’s behavior at that time. This process is like finding a needle in a haystack. Remarkably, many new findings are rapidly expanding the limits of what we consider the human experience. Aside from bones that tell us where people lived and what they looked like at certain times, artifacts include tools, art, medical and chemical implements, and housewares. Unfortunately, there are no artifacts from 8 million to 3.7 million years ago. Discoveries can never prove that people didn’t exist earlier. The important question is: how long have people been smart?
The major way we learn about human evolution is finding fossils of bones and teeth as well as artifacts. These fossils and artifacts are dated by chemical and physical techniques and then analyzed for what they might imply about people’s behavior at that time. This process is like finding a needle in a haystack. Remarkably, many new findings are rapidly expanding the limits of what we consider the human experience. Aside from bones that tell us where people lived and what they looked like at certain times, artifacts include tools, art, medical and chemical implements, and housewares. Unfortunately, there are no artifacts from 8 million to 3.7 million years ago. Discoveries can never prove that people didn’t exist earlier. The important question is: how long have people been smart?
 A previous post noted that human ancestors engaged in intelligent behavior from a million years ago, when there were 20,000 to 50,000 people on Earth; this includes advanced Pacific Ocean seafaring and the controlled use of fire. Please refer to the previous post for a detailed summary of information on human ancestors. This post describes new findings in the past year, as well as a timeline incorporating the old and new findings. A recent article in Nature estimated that the modern human mind could have existed 500,000 years ago. But, it could be much earlier than this. Recent findings have, also, filled in details of flourishing cultures all over the globe long before “recorded history,” such as Stonehenge 5000 years ago.
A previous post noted that human ancestors engaged in intelligent behavior from a million years ago, when there were 20,000 to 50,000 people on Earth; this includes advanced Pacific Ocean seafaring and the controlled use of fire. Please refer to the previous post for a detailed summary of information on human ancestors. This post describes new findings in the past year, as well as a timeline incorporating the old and new findings. A recent article in Nature estimated that the modern human mind could have existed 500,000 years ago. But, it could be much earlier than this. Recent findings have, also, filled in details of flourishing cultures all over the globe long before “recorded history,” such as Stonehenge 5000 years ago.
This post will update new information that expands human history in many directions including art, tools and seafaring. In addition there is evidence that ancestors possibly left Africa millions of years ago, evolved further in Eurasia and then returned to Africa around 2 million years ago. What would it mean that very ancient people had modern minds in very different circumstances?
Human Evolution Theories Inadequate
 It is important to note that many popular theories assume that humans evolved because of particular environments. These speculative theories have been termed “paleofantasies.” For example, it has been discovered, recently, that the Sahara desert was a fertile region 5000 years ago with grasslands, vegetation, and roaming wildlife. There was a humid period lasting from 11,000 years ago, which very suddenly ended 5000 years ago. The drying occurred in the span of two hundred years.
It is important to note that many popular theories assume that humans evolved because of particular environments. These speculative theories have been termed “paleofantasies.” For example, it has been discovered, recently, that the Sahara desert was a fertile region 5000 years ago with grasslands, vegetation, and roaming wildlife. There was a humid period lasting from 11,000 years ago, which very suddenly ended 5000 years ago. The drying occurred in the span of two hundred years.
With such dramatic climate changes occurring in hundreds of years, it is impossible to consider one particular environment critical for human evolution, when the details are not known over hundreds of thousands of years (or millions of years.) Also, recent fossil findings are altering notions of where human evolution occurred. For example, there is now evidence that ancestors might have migrated out of Africa to Eurasia, then migrated back 2 million years ago. It is simply impossible, currently, to say how or why human evolution occurred, except that people were very smart much longer than previously known.
Seafaring
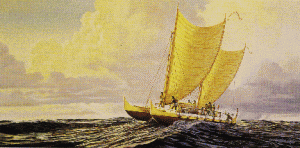 Seafaring involves building boats and rafts, as well as navigating seas, and then surviving in a new land. It is very advanced cognitive behavior. Until last year travel to Flores Island in Indonesia was known to have occurred 74,000 years ago. Now, it has been discovered that this travel occurred at least 1.1 million years ago. Such a trip would tax any modern human.
Seafaring involves building boats and rafts, as well as navigating seas, and then surviving in a new land. It is very advanced cognitive behavior. Until last year travel to Flores Island in Indonesia was known to have occurred 74,000 years ago. Now, it has been discovered that this travel occurred at least 1.1 million years ago. Such a trip would tax any modern human.
Other remarkable new data shows that people traveled to the Island of Crete in the Mediterranean at least 170,000 years ago—discovered by findings of hand axes, tetrahedral picks, and cleavers on the island. Similar tools are, also, found from 110,000 years ago on the Greek island Ionia.
Three thousand seafaring South East Asian people reached Australia 50,000 years ago. This large movement of people probably needed large ships. Also, there was a great variation in the people who travelled there. The first European settlement in Australia was in 1788 when there were 1 million aboriginal people present.
Tools
 Another dramatic finding is that complex spears put together with multiple parts were recently found in South Africa from 500,000 years ago, 200,000 years earlier than previously thought. Stone tipped javelins are found 280,000 years ago, 200,000 years older than before.
Another dramatic finding is that complex spears put together with multiple parts were recently found in South Africa from 500,000 years ago, 200,000 years earlier than previously thought. Stone tipped javelins are found 280,000 years ago, 200,000 years older than before.
Analysis of the best tools from 10 sites between 284,000 to 7,000 years ago all show equivalent complex techniques used to manufacture the best tools of the era. Modern humans would find it extremely difficult to duplicate these tools. Not only were cavemen better tool technicians than modern people, they also have been shown to be able to draw four legged animals better than modern artists.
Neanderthals, considered to be less intelligent than other homo species, must also be re evaluated. They made bird bark glue fastening stone to wood handles 300,000 years ago. They made engraved patterns on iron oxide, bone awls, hide clothing and shell beads 110, 000 years ago. At 79,000 years ago, they were excellent pyro technologists and chemists. All of these feats show advanced cognition.
Art
 Cave art and symbolic artifacts in Europe flourished from 40,000 years ago, which encouraged a theory of advanced cognition originating in Europe. However, this year findings in Spain, China, South Africa, and Siberia show advanced artistic artifacts much earlier. In South Africa ostrich shell beads and etched ochre were 30,000 years earlier. In Morocco similar art were from 80,000 years ago, in Beijing 34,000 years ago and in South America 16,000 years ago. Recently, in Israel, a Berekhat Ram figurine from 230,000 has been identified, although it is considered controversial.
Cave art and symbolic artifacts in Europe flourished from 40,000 years ago, which encouraged a theory of advanced cognition originating in Europe. However, this year findings in Spain, China, South Africa, and Siberia show advanced artistic artifacts much earlier. In South Africa ostrich shell beads and etched ochre were 30,000 years earlier. In Morocco similar art were from 80,000 years ago, in Beijing 34,000 years ago and in South America 16,000 years ago. Recently, in Israel, a Berekhat Ram figurine from 230,000 has been identified, although it is considered controversial.
Summary of Findings This Year – How Long Have People Been Smart
- A skull from Chad with a human style brain, distinct from chimps, was discovered that is now the oldest human ancestor at 7 million years ago.
- In Kenya a human ancestor walked upright at 6 million years ago.
- A finding showed modern middle ear bones 3 million years ago, which implies communication.
- A series of very variable skulls 2 million years ago in Georgia mean that what have been considered different species might just be variations of the same species
- Sediba from South Africa 2 million years ago had modern jaws and teeth and an unknown type of upright walking.
- Fossils from 1.8 million years ago in Dmanisi, Georgia raise questions of ancestors evolving in Eurasia then migrating back to Africa.
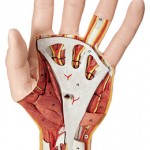
- A modern hand was found at 1.7 million years ago that could use advanced tools. Other tools were as early as 2.7 million years ago.
 Hands from 1.5 million years ago had bone structures for great dexterity, half a million years earlier than previously known.
Hands from 1.5 million years ago had bone structures for great dexterity, half a million years earlier than previously known.
- At 1.3 million years, an old man spent much of his time in the trees.
- 1 million years ago ancestors had a nearly modern foot.
- Stone tools were found from 840,000 years ago on Flores Island, Indonesia, where “hobbits” lived from 1.7 million to 550,000 years ago. They, also, were found to have additional wrist bones, which probably makes them a different species. Australapiths evolved in Africa from 4 million to 2.8 years ago. Did one leave Africa to become a hobbit?
- DNA from ancestors 400,000 years ago is similar to the Denisovan’s who were thought to live only 80,000 years ago.
- Stone tipped javelins 280,000 years ago, 200,000 years older than before.
- Neandertals were much more talented than previously thought with special bone tools to smooth animal hides like modern leather workers. Significantly, they invented string 90,000 years ago. Their houses were very neat and organized and they buried their dead.
- DNA of a boy from Siberia 24,000 years ago included European and Asian qualities. This probably means that Native Americans probably have such DNA also.
- Ancestors left Africa earlier than thought and evolved elsewhere. Humans may have appeared in Asia, not Africa.
- 1000 years ago, healers in Peru practiced trepanation—a surgical procedure that involves removing a section of the skull for many ailments, from head injuries to heartsickness.
Large Stone Monuments in Europe
 There is new evidence that culture flourished in many parts of the world before “recorded history.” This year brought great new understanding of Stonehenge and similar large stone structures throughout Europe.
There is new evidence that culture flourished in many parts of the world before “recorded history.” This year brought great new understanding of Stonehenge and similar large stone structures throughout Europe.
Large stone monuments were first built 11,000 years ago in the shape of animals in Turkey at Gobekli Tepe. These monuments occurred at the same time as the spread of farming, domestication of animals and pottery. Possibly, this is because hunter gatherers did not change the natural environment, whereas farmers did. In Europe farming and stone monuments started 8500 years ago.
The first very large stone monuments were on Orkney Islands, north of Scotland, 5000 years ago. This activity was related to large gatherings of more than 10,000 people from all over Europe. The first monuments involved circular dirt mazes. Then, after 400 years, parallel banks of dirt surrounding the circular maze. Then, 300 years later large stone monuments next to a “henge”, which is defined as a dirt bank with stones inside it or around it.
Orkney had 12 large buildings used for 1000 years. Stones were dragged from at least 10 miles away. Starting from these, monuments were built all through Ireland and Britain.
The last and greatest stone monument is Stonehenge. The site was first visited 7500 years ago, but, settled 5000 years ago. There are two large structures, the second being Durrington Walls. Both were built 4600 years ago. Durrington Walls was for the living with findings of 80,000 cattle and pig bones and no human bones. Stonehenge was for cremation of the dead with many human remains from all over Europe. Both have roads to the river. Stones came from many far away places as an act of cooperation and competition—who could drag the biggest stone from farthest away to help the cathedral. Nearby were elaborate tombs and stone houses for the elite with central hearths, stone beds and dressers.
For comparison, a timeline of early civilizations are listed, along with projected Biblical events.
- 11,000 ya – Large stone monuments in Turkey
- 8500 ya – Small stone monuments in Europe
- 6000 ya – Adam and Eve
- 5100 ya – Egyptian hieroglyphics
- 5000 ya – Orkney monuments
 4700 ya – Egyptian pyramids
4700 ya – Egyptian pyramids- 4600 ya – Stonehenge
- 4000 ya – Ancient Bablylonia
- 4000 ya – Earliest Chinese dynasties
- 4000 ya – Old Testament Abraham
- 3500 ya – Old Testament Exodus
- 3500 ya – Earliest Rig Veda
- 3000 ya – Ancient Greece
- 2600 ya – Buddha
An Inexact Timeline of Human Evolution Including Latest Information
Mya = Million years ago
8 to 2.5 mya
— — Common ancestor to austraolopithecines
— — Brain size of apes
8 mya to 3.7 – No artifacts
7 mya – Chad skull with human style brain
 6 mya – Kenya ancestor walked upright
6 mya – Kenya ancestor walked upright
3.4 mya – Fossils of second hominid line living alongside Lucy
— — More in the trees than Lucy
3 mya – Modern middle ear bones implies communication
3 mya – Marked animal bones in Ethiopia
3 mya – First stone tools – Mutation – GADD45G – Larger Brain
2.6 mya – More advanced flake tools for stripping meat
2.3 mya – Homo habilis – head 1.5 x larger
 2 mya – Modern shoulders for accurate throwing
2 mya – Modern shoulders for accurate throwing
2 mya – Great variation in skull in one site suggest other findings one species
2 mya – Sediba shows modern jaws and teeth and unusual upright walking
2 mya – Australopithecus sediba ate tree bark
2 mya – Mutation SRGAP2 – Increased signal processing
1.9 mya to 200 kya – Homo erectus – head 2 x larger
1.95 mya – multiple homo lineages in Kenya
1.8 mya – Dmanisi, Georgia skulls – could ancestors have evolved in Eurasia then return to Africa
1.76 mya – Bifacial stone tools in Kenya
1.7 mya – Modern hand for advanced tools
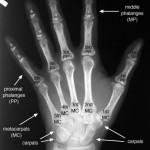 1.5 mya – Hands with bone structure for greater dexterity, 500 kya earlier than thought
1.5 mya – Hands with bone structure for greater dexterity, 500 kya earlier than thought
1.3 mya – An old man spent much time in trees
1.1 mya – Travel by sea to Flores Island, Indonesia
1 mya – Homo heidelbergensis – head 3x larger
 1 mya – Mutation HAR1 – Cortex expansion
1 mya – Mutation HAR1 – Cortex expansion
— — Mutation FOXP2 – amino acid changes
1 mya – Burned bone and plants showing use of fire
— — Controlled use of fire South Africa
Kya = Thousand years ago
 840 kya – Stone tools on Flores Island – also additional wrist bones
840 kya – Stone tools on Flores Island – also additional wrist bones
800 to 30 kya – Neanderthals and Denisovans larger heads
500 kya – Mutation – MEF2A – Delayed Synapses PFC
500 kya – Advanced composite spears
— — Stone tips on wood shafts, South Africa
400 kya – DNA of ancestors similar to Denisovans – thought to be 80 kya
280 kya – Stone tipped javelin – 200 kya earlier than thought
230 kya – Controversial Berekhat Ram figurine
200 kya – Homo sapiens sapiens
200 kya – Mutation – FOXP2 – regulation Language
170 kya – Sea travel to Crete
 164 kya – Heat-treated stone tools, South Africa
164 kya – Heat-treated stone tools, South Africa
164 kya – low-grade fire to change the silcrete rock into a harder form.
130 kya – Migration from Africa to Eurasia started
110 kya – Sea travel to Ionian Greek islands
100 kya – Engraved iron oxide (ocher) South Africa
80 kya – Symbolic cave work, Blombos, South Africa
80 kya – art in Morocco
77 kya – Insect repellant bedding, South Africa
71 kya – Projectile points, South Africa
70 kya – ostrich shell beads and etched ochre
43 kya – Flutes in Germany
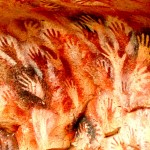 42 kya – 50 Neanderthal cave paintings in Spain
42 kya – 50 Neanderthal cave paintings in Spain
41 kya – Cave paintings in Spain
40 kya – Shell bead necklace, cave wall paintings many animals
— — New and better stone, bone tools in Europe
40 kya – Cave 30 cm ivory statuette of man/lion head, Germany
34 kya – Art in Beijing
32 kya – Cave ivory animals horse, mammoth, bison, Germany
24 kya – Siberian DNA from Europe and Asia – relevant to Native Americans
20 kya – Advanced figures, and cave paintings in Lascaux, France
 20 kya – Statue, Venus of Lespugue
20 kya – Statue, Venus of Lespugue
16 kya – Art in South America
13 kya – Early Americans with tools
11 kya – First large stone monuments – with farming, animal domestication, pottery
8.5 kya – Turkey, Greece – forage & farmers co exist 200 yrs.
8.5 kya – Stone monuments throughout Europe
7.5 kya – Manipulating environment – long before farming
7.5 kya – Visitors at site of Stonehenge
— — Evidence of efforts for increasing plant value
 7 kya – Northern Europe made cheese
7 kya – Northern Europe made cheese
5 kya – Many large monuments Orkey, Island and throughout Britain
5 kya – With Large monuments, huge festivals of varied people, elite houses with hearth
5 kya – Maize in diet of Peru
4.6 kya – Stonehenge
1 kya – brain surgery in South America